WHO (World health organization) defines overweight and obesity as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. Obesity is a global health problem. At least 2.8 million adults die each year as a result of being overweight or obese. In addition, 44% of the diabetes burden, 23% of the ischaemic heart disease burden and between 7% and 41% of certain cancer burdens are attributable to overweight and obesity. On average, obesity reduces life expectancy by six to seven years, while severe obesity (BMI > 40 kg/m2) reduces life expectancy by ten years. In India the obesity is rapidly rising among the general population. 1 in 5 adults are overweight in India.
People with obesity have a higher chance of developing these health problems:
In addition to these health problems, obesity causes cancer. Every 5 kg/m2 increase in BMI increases the risk of endometrial cancer by 62%, gallbladder cancer by 31% and kidney cancer by 25%. Severe obesity also interferes with the routine work and socialization.
Most patients with severe obesity cannot lose and maintain weight with nonsurgical treatment. Lifestyle modification and currently available drugs are associated with a modest weight loss (average 5 kg) which is poorly sustained.
Studies have shown that surgery offers the only permanent and sustained weight loss in comparison to other options. These surgeries are done when diet and exercise have failed to reduce the weight to an optimum level. The operations to lose weight are called bariatric surgery. This operation make changes in the digestive tract and limits the amount of food which can be eaten and/or reduces the absorption of nutrients. In addition, they make hormonal changes which improves satiety and reduce weight.
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a calculation to know the weight in relation to the height. It is defined as a person's weight in kilograms divided by the square of his height in meters (kg/m2). It is the most commonly used formula to determine the grade of obesity.
People with obesity have a higher chance of developing these health problems:
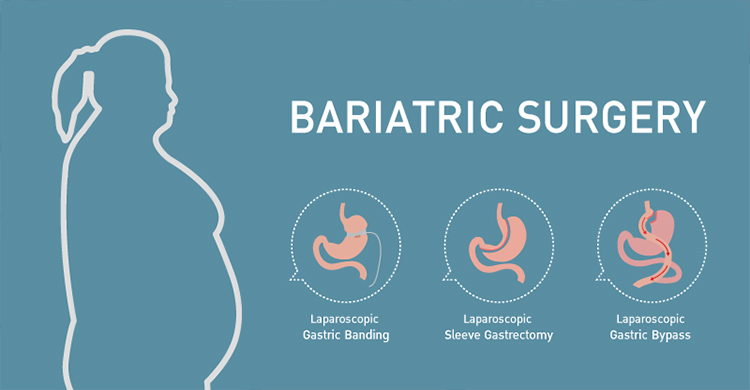
The commonly done operations in India include:
These operations helps reduce weight and reduces risk of associated diseases. But not all excess weight will be lost; only 50-75% of excess weight loss is expected. More than 90 percent of individuals are successful in maintaining 50 percent or more of their excess weight loss following surgery.
The surgery improves and resolves most of the obesity related diseases in majority of the individuals. For example diabetes improves in more than 85 percent and resolves in 78 percent. Hyperlipidemia improves in 97% and sleep apnea in 81%. In addition to improvement in health and longevity overall quality of life is improved. Several large studies have shown that risk of death is reduced following surgery.
Before surgery cardiovascular, pulmonary and endocrine systems has to be carefully evaluated. A psychological evaluation is also an important part of preparation. Counselling is done about dietary and nutritional issues related to surgery.
You will feel satisfied with eating smaller portions, so you will be able to limit the amount of food you eat at one time. You will need to change your overall diet and eating habits, including drinking at least eight cups of water per day, chewing your food completely and consuming smaller portions. Since the amount of food you consume is decreased, you need to eat only quality food.
There is a need for regular lifelong follow-up after the surgery. Strict compliance with the dietary, exercise and lifestyle modifications is required before and after the surgery.
