LIVER CANCER
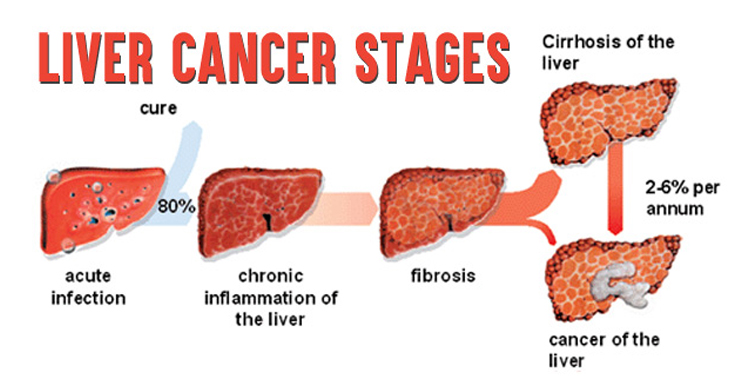
Liver is vulnerable to several types of cancers, such as Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma and Hepatoblastoma. Hepatocellular Carcinoma is the most prevalent form of liver cancer that originates from Hepatocyte, the primary cells found in liver. Individuals with chronic liver issues like cirrhosis are more prone to this dreaded condition. Atypical Hepatocellular Carcinoma screening involves blood tests, standard imaging tests and liver biopsy. Advanced imaging tests, including Magnetic Resonance Elastography may also be used.
As per the TNM system for staging, liver cancer is categorized into four stages and several sub-stages.
SYMPTOMS
The general prognosis of liver cancer is awful. The symptoms remain dormant in the early stages and when they surface, the disease becomes virtually uncontrollable. The standard signs and symptoms of liver cancer may include, but not limited to, liver overgrowth, white-collared stools and skin turning yellow. Other non-specific symptoms include sudden and drastic weight loss, appetite loss, nausea, vomiting, constant fatigue and atypical swelling. These symptoms are called nonspecific, as other chronic disorders may trigger similar effects.
Treatment
The treatment options for liver cancer are –
